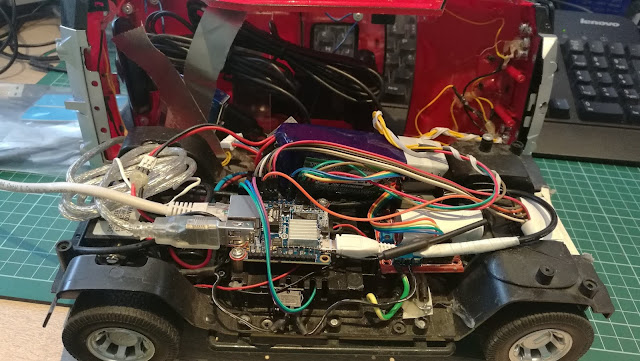
This is a followup of my original post.
I have added a voltage readout of the battery in my toy car. It looks like this on client applications:
Voltage is read using MCP 3008 A/D converter:
Here is the layout:
The zero argument from the read_adc function is the number of the channel. In my case, I have connected the voltage from the battery to the pin 1 of the MCP3008, which is channel 0. Since the voltage of the fully charged battery can exceed 10V, I had to reduce the voltage:
I have extended my original Python server for the toy car to accept a telemetry request (string 't' as a telemetry request) and to send the voltage (currently it is just the voltage), as a JSON string:
Java Swing application
Android application
Voltage is read using MCP 3008 A/D converter:
MCP 3008 A/D converter pinout
Here is the layout:
- connect pins 16 (Vdd) and 15 (Vref) to the 3.3V pin of your GPIO port of your Orange Pi, or Raspberry Pi (they are pin-to-pin compatible),
- connect pins 14 (Agnd) and 9 (Dgnd) to the GND pin of your GPIO port,
- connect pin 13 (CLK) to the pin 23 of the GPIO port,
- connect pin 12 (Dout) to the pin 21 of the GPIO port,
- connect pin 11 (Din) to the pin 19 of the GPIO port,
- connect pin 10 (CS) to the pin 24 of the GPIO port.
Make sure that SPI is enabled on your device. On my Orange Pi, it is was enabled by default. On Raspberry Pi, you need to start the raspi-config and enable SPI from the menu.
If the SPI is properly enabled, you will be able to see two files in the /dev folder of your Pi:
/dev/spidev0.0 and /dev/spidev1.0.
I have used Adafruit MCP library from this location.
When you download and install this library, you will use it by importing following modules:
import Adafruit_GPIO.SPI as SPI
import Adafruit_MCP3008
Then you need to set it up:
# Hardware SPI configuration:
SPI_PORT = 1
SPI_DEVICE = 0
mcp = Adafruit_MCP3008.MCP3008(spi=SPI.SpiDev(SPI_PORT, SPI_DEVICE))
On my Raspberry Pi, I have set the SPI_PORT variable to zero (0). On my Orange Pi, I had to set it to one (1). You can then read the voltage this way:
voltage = mcp.read_adc(0)
The zero argument from the read_adc function is the number of the channel. In my case, I have connected the voltage from the battery to the pin 1 of the MCP3008, which is channel 0. Since the voltage of the fully charged battery can exceed 10V, I had to reduce the voltage:
Voltage reduction
I have extended my original Python server for the toy car to accept a telemetry request (string 't' as a telemetry request) and to send the voltage (currently it is just the voltage), as a JSON string:
elif text == 't':
voltage = mcp.read_adc(0)
c.send("{ \"voltage\": " + str(voltage) + '}\n')
My client applications (both Java Swing and Android) send periodically this request string and receive a JSON string. Then they parse the JSON string, extract the voltage, and display it on the screen.